1. Introduction
This document describes the
-
test environment,
-
the hardware used,
-
the procedures applied and
-
the results of the test.
The test has been executed as part of the e-Spirit module certification process.
2. Test environment
2.1. FirstSpirit Server Configuration
The FirstSpirit Server and the TranslationStudio Application Service were both hosted on the same physical machine with the following software and hardware capabilities:
-
System
Debian GNU/Linux 9 (stretch) (amd64) -
CPU
Intel® Core™ i3-3220T CPU @ 2.80GHz -
Memory
8.0 GB -
Java Version
Java HotSpot 64-Bit Server VM Version 1.8.0_191-b12 -
FirstSpirit Server
Version 5.2.190105.78007
2.2. TranslationStudio
A docker container based on debian:buster with openjdk-11-jdk python3 python3-pandas python3-matplotlib installed was used to run TranslationStudio.
TranslationStudio was started using the following memory parameters:
-XX:GCLogFileSize=10485760
-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
-XX:HeapDumpPath=log/crash.hprof
-XX:InitialHeapSize=129219968
-XX:MaxHeapSize=2067519488
-XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles=10
-XX:+PrintGC
-XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps
-XX:+UseCompressedClassPointers
-XX:+UseCompressedOops
-XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation
-XX:+UseParallelGC3. Test Procedure
The following test consisted of the consecutive translation of datasets and pages.
3.1. Translation of Datasets
The aim of the procedure applied is to forwards 10,000 datasets simultaneously and to complete the entire translation process.
The test used a special Translation Memory System connector which took the source translatable XML and forwarded it to the import process after the translation status had been requested. The files were not modified in any way.
The procedure consists of the following parts:
-
If found, delete previous 10,000 datasets
-
Create 10,000 datasets
-
Execute a dataset translation workflow
-
Create task tickets representing 20 datasets each
-
Forward the translation requests to TranslationStudio Application
-
Store the translation requests in the TranslationStudio database
-
Create and process a single translation job containing 10,000 datasets
-
Export the datasets to the file system
-
Create translatable XML files
-
Create additional message files for each translatable XML (i.e. querying all task tickets)
-
Forward the translatable XML files to the Test Connector
-
Query status of each translatable file and receive a
translation completemessage -
Obtain the translated XML files
-
Import the translatable XML file into FirstSpirit
-
Remove task ticket in FirstSpirit again.
Steps 1-2 were part of a special workflow executed using the ServerManager.
3.2. Translation of Newly Created Pages
The aim of the procedure applied is to forwards 10,000 newly created pages simultaneously and to complete the entire translation process. The procedure consists of the following parts:
-
Remove (if necessary) and create 10,000 pages
-
Execute the page folder workflow
-
Create 10,000 task tickets
-
Store the translation requests in the TranslationStudio database
-
Forward translation request to the TranslationStudio Application
-
Create and process a single translation jobs containing 10,000 pages
-
Export the registered pages to the file system
-
Create translatable XML files
-
Create additional message files for each translatable XML
-
Forward the translatable XML files to the Test Connector
-
Query status of each translatable file and receive a
translation completemessage -
Obtain the translated XML files and add timestamp to each TEXT and DOM child node.
-
Import the translatable XML file into FirstSpirit
-
Update/Check the language flag for each imported FirstSpirit page and section
-
Remove task ticket in FirstSpirit again.
Steps 1-2 were part of a special workflow executed using the ServerManager.
Preview files were not created since they do not add significant load to the TranslationStudio Application
3.3. Translation of Already Translated Pages
The aim of the procedure applied is to forwards 10,000 already existing (i.e. translated) pages simultaneously and to complete the entire translation process. The procedure consists of the following parts:
-
Execute the page folder workflow
-
Create 10,000 task tickets
-
Store the translation requests in the TranslationStudio database
-
Forward translation request to the TranslationStudio Application
-
Create and process a single translation jobs containing 10,000 pages
-
Export the registered pages to the file system
-
Create translatable XML files
-
Create additional message files for each translatable XML
-
Forward the translatable XML files to the Test Connector
-
Query status of each translatable file and receive a
translation completemessage -
Obtain the translated XML files and add timestamp to each TEXT and DOM child node.
-
Import the translatable XML file into FirstSpirit
-
Update/Check the language flag for each imported FirstSpirit page and section
-
Remove task ticket in FirstSpirit again.
Steps 1-2 were part of a special workflow executed using the ServerManager.
Preview files were not created since they do not add significant load to the TranslationStudio Application
3.4. End of Test Phase
To check for memory recovery and potential memory leaks, a garbage collection is performed at the end of the tests. This is followed by a 45min waiting period.
A second garbage collection is performed and after a second, final 45min waiting period, the application is shutdown programmatically.
3.5. Results
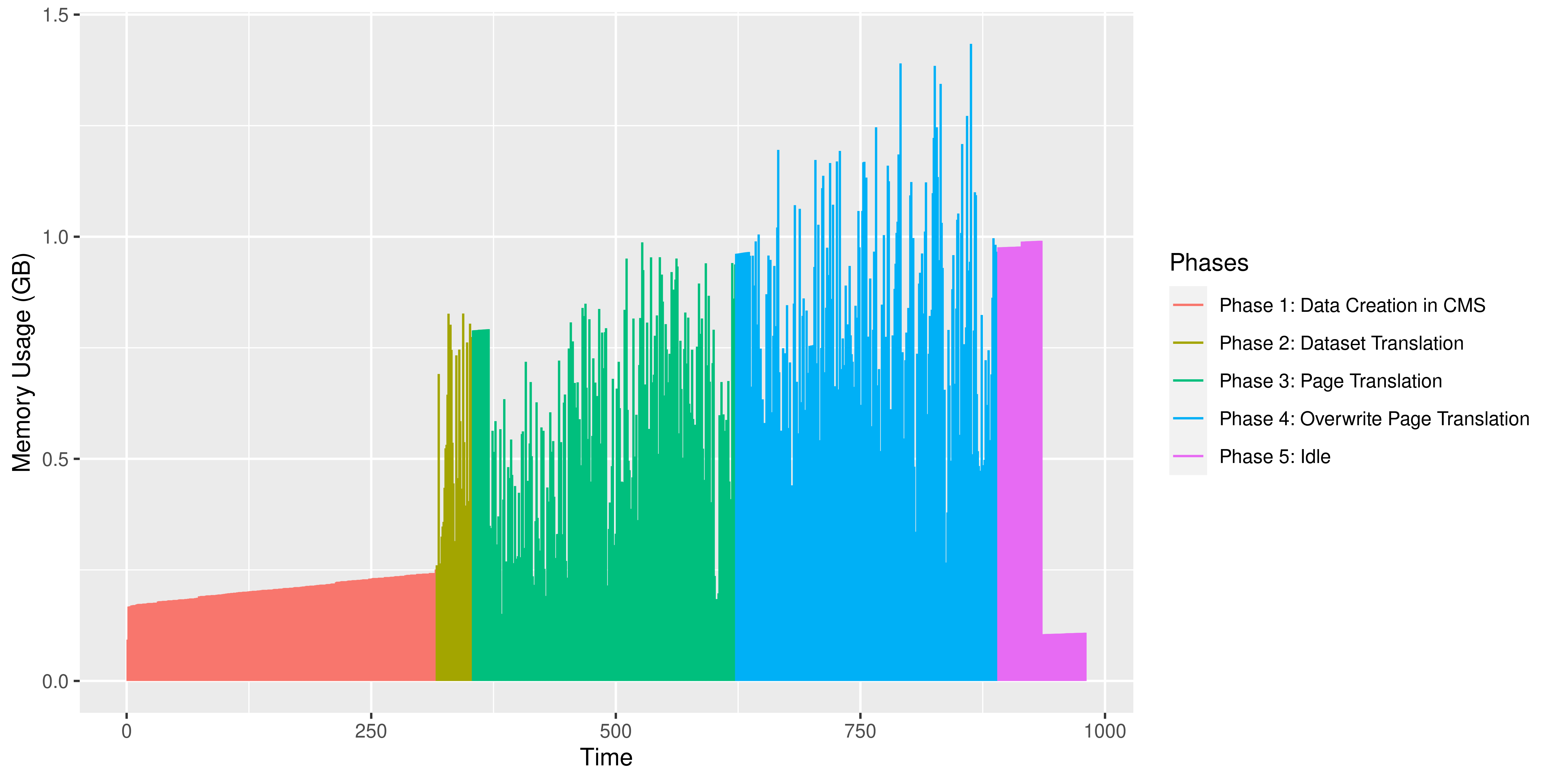
The test result is summarised below. The memory consumption refers to the TranslationStudio Application only.
| Result | Datasets | Pages (new pages) | Pages (already translated) |
|---|---|---|---|
Duration |
0h 38m |
4h 28m |
4h 28m |
Number of Pages/Datasets |
10,000 |
10,000 |
10,000 |
Pages/Datasets per XML file |
10,000 |
400 |
400 |
XML files processed |
1 |
25 |
25 |
Embedded database size |
13 MB |
||
Peak memory consumption |
1.21 GB |
||
Average memory consumption |
0.41 GB |
The following graph illustrates the memory consumption during the entire test up until 60mins after the last XML has been imported.
The areas of zero memory consumption are not considered in the average above but only used to visualize the end of a test and the beginning of a subsequent test.